Sound Advice | Loudspeaker placement part 2: Low frequency cancellation
In the quick tip, we talk about low frequency cancellation when loudspeakers are placed within a certain proximity to walls and surfaces.
Today's Lesson
While placing a loudspeaker against a wall will cause low frequency build-up, placing a loudspeaker within a certain proximity to walls and surface can have other adverse effects. Primarily, a phenomenon known as low frequency comb filtering cancelation.
What this means is that at frequencies where the distance from a wall is equal to one quarter of the sound wavelength emitted, the wall reflection is out of phase with the loudspeaker forward radiation. As a result, the sound reflected by the wall at this specific frequency will cancel the loudspeaker’s forward radiation of the same frequency.
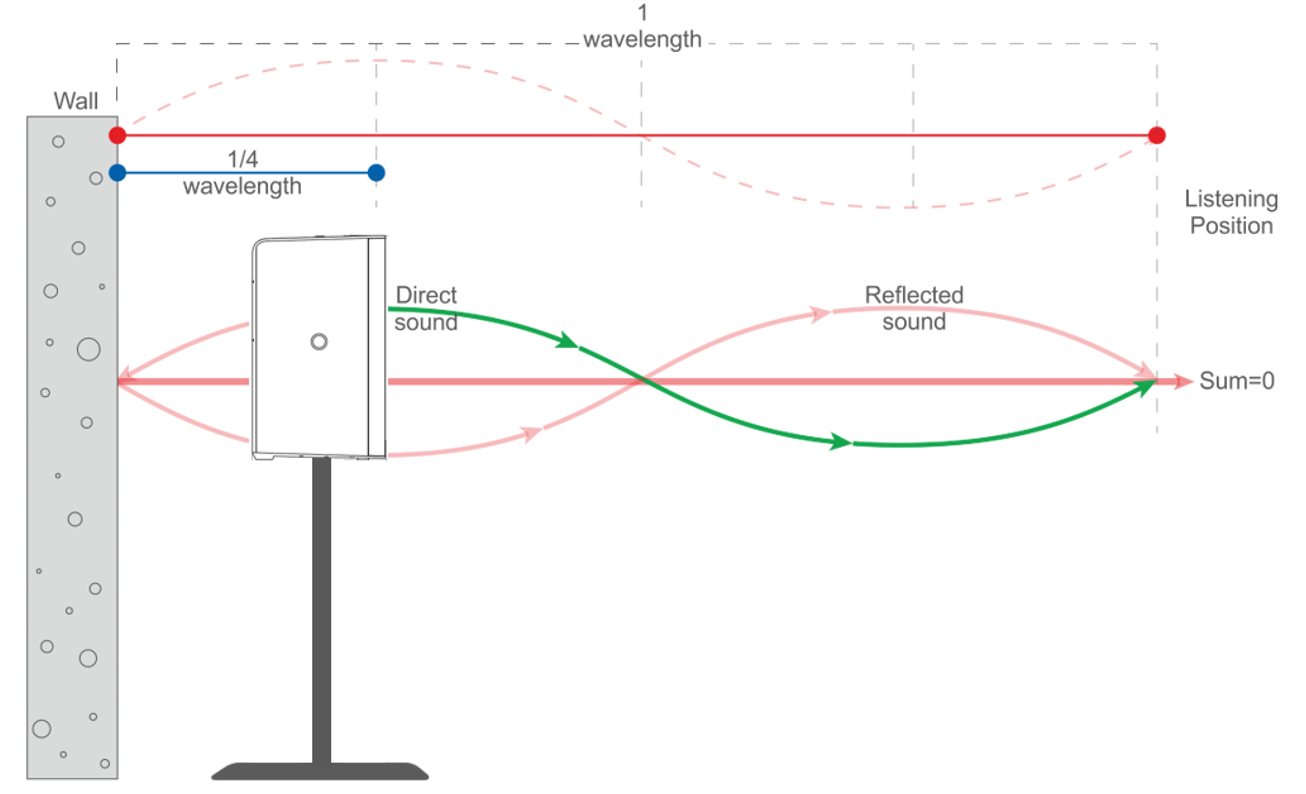
How far from the back wall should your PA system be to avoid cancellations? To figure this out, take the lowest frequency in your loudspeakers range and calculate the ¼ wavelength distance of that frequency. For example, the K12.2 extends down to 45 Hz. The quarter wavelength of 45 Hz is 1.9 m or 6.25 ft.
So, as long as that K12.2 loudspeaker is further than 1.9 m or 6.25 ft. from any walls, you will ensure that no cancellation will occur and the full bandwidth of the loudspeaker will be reproduced.
For more lessons and videos, see our QSC YouTube page.